DN1200
Cylindrical fixed full-welded ball valve
Fixed Ball Structure: In a fixed ball structure, the ball has an upper and lower rotating shaft. The lower part of the ball is embedded with a bearing, fixed by the lower stem, and the upper part is connected to the upper stem. The ball can only rotate along the vertical axis of the valve passage; it cannot move laterally like a floating ball valve. Therefore, when the fixed ball valve is in operation, the pressure of the upstream fluid and the spring force press the seat tightly against the ball, forming a reliable upstream seal. The fixed ball valve has a DBB function, meaning it can simultaneously shut off the medium upstream and downstream of the pipeline, providing safe and reliable valve sealing.
Product Classification:
Key words:
Overview
Floating Ball Structure: In a floating ball valve, the ball is free-floating within the valve body. Under fluid pressure, the ball is tightly pressed against the outlet seat, creating a downstream seal. This structure is characterized by its simplicity and excellent sealing performance.
Fixed Ball Structure: The ball in a fixed structure has upper and lower rotating shafts. A bearing is embedded in the lower part of the ball, fixed by the lower stem, and connected to the upper stem at the top. The ball can only rotate vertically along the valve passage axis and cannot move laterally like a floating ball valve. Therefore, during operation, the pressure of the upstream fluid and the spring force press the seat tightly against the ball, creating a reliable upstream seal. The fixed ball valve has a DBB function, meaning it can simultaneously shut off the medium from both upstream and downstream, ensuring safe and reliable valve sealing.
Product Features
• Low Flow Resistance Coefficient
The pressure loss of a ball valve at the nominal flow rate is the lowest among all valve types, equivalent to the flow resistance coefficient of a pipe of the same length, virtually zero; Our company's reduced-bore ball valves, through fluid analysis and theoretical calculations, have a flow path design that maximizes the valve's flow capacity and minimizes the flow resistance caused by the reduced-bore section.
• Bi-directional Sealing
The ball valve is unaffected by the direction of the fluid medium; either end of the valve can serve as the upstream end. The fixed ball valve can simultaneously shut off fluid media from both upstream and downstream.
• Excellent Sealing Performance
Double seat, bi-directional sealing; the seat seal consists of VITONB+, a non-metallic polymer suitable for different pressure levels, + hard seal, ensuring bubble-tight sealing (i.e., zero leakage) under different pressure differentials; sealing is safe and reliable.
• Long Service Life
The non-metallic sealing surfaces have good lubricity, resulting in minimal friction and wear with the ball; multi-stage sealing, along with spring pre-tightening, ensures safe and reliable sealing, thus extending the service life of the ball valve.
Product Installation
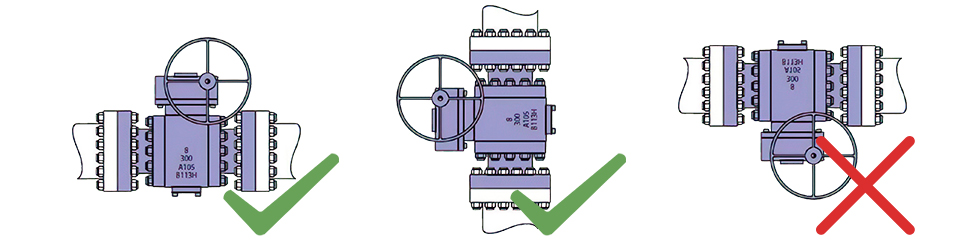
1. The pipes connected to the valve must be thoroughly cleaned to prevent iron filings, sand, welding slag, and other debris from damaging the valve sealing surfaces.
2. This series of ball valves can be installed in any position; either end of the valve can serve as the upstream end; both horizontal and vertical installation are acceptable, but upside-down installation is prohibited to prevent stem corrosion;
3. During installation, the valve should be kept fully open (factory adjusted), otherwise, damage to the valve may occur; Warning: Do not leave the valve in a half-open/half-closed state.
4. The center of the valve must align with the center of the pipe and pipeline before welding installation:
5. Welding connections should be carried out according to welding procedures approved by the welding procedure qualification; during installation welding, prevent welding slag and welding beads from entering the valve cavity and damaging the sealing surface. The valve should be in the fully open position during installation, otherwise valve damage may occur. Warning: For butt-welding end ball valves, do not install while the valve is closed. If the valve must remain closed, apply grease to the exposed ball surface to protect it from damage by spattering weld slag.
6. During preheating, welding, and stress relief, the temperature at any point on the valve body 75mm away from the weld seam must not exceed 200℃. Please use a thermometer to check the temperature.
7. During valve installation, ensure that the valve cavity remains clean to prevent debris from entering the cavity;
8. After welding the end valves, a visual inspection or non-destructive testing should be conducted to confirm that there are no cracks, welds, or undercuts. Nondestructive testing of the weld seam should be performed as required:
9. For valves with actuators, the electrical, pneumatic, and hydraulic lines should be connected according to the wiring diagram or piping diagram in the instructions. Confirm the correctness of the wiring before switching on; the factory has adjusted the open and closed positions of the valve; no readjustment is necessary.
10. The actuators of underground pipeline valves cannot be immersed in water or mud to prevent damage to the actuators;
Note: If the valve is unavoidably immersed in water or mud for a long time, please inform the manufacturer in advance so that the manufacturer can take countermeasures in advance.
11. When installing large-diameter welded ball valves, the weight of the valve should not be entirely borne by the pipeline; fixed supports or brackets should be provided for support.
12. Valves with external insulation requirements should have their protective layer installed before the medium is introduced. Fixed supports or brackets should be provided for support.
12. Valves with external insulation requirements should have their protective layer installed before the medium is introduced.
Design Parameters
Design and Manufacture: GB/T12237, GB/T37827, GB/T12224, ASME B16.34
Inspection and Testing: GB/T13927, JB/T9092, ISO 5208
Fire Test: GB/T26479, API 6FA, API 607
Pressure Rating: 1.6Mpa~4.0Mpa;
Nominal Diameter: DN15~1400mm;
Applicable Media: Water, gas, oil, etc.;
Applicable Temperature: -29℃~200℃.
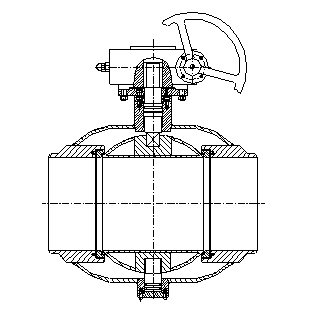
Main Component Material Details
| Part Name | Standard Material | Stainless steel material | Forging material |
| Valve body | 20# | 304 | A105 |
| Valve cover | 20# | 304 | A105 |
| Ball | 304 | F304 | F304 |
| Valve seat | A105+ENP | 304 | A105+ENP |
| Valve seat sealing ring | RPTFE | RPTFE | RPTFE |
| Stem | 20CR13 | 304SS | 20CR13 |
| Stuffing box | 20# | 304 | A105 |
| Spring | INCONEL X-750 | INCONELX-750 | INCONEL X-750 |
| Pivot | 20CR13 | 304SS | 20CR13 |
| Upper and lower diameter | 20# | 304 | A105 |
| Sliding bearing | 304+MOS2+PTFE | 304+MOS2+PTFE | 304+MOS2+PTFE |
| O-ring | Fluororubber | Fluororubber | Fluororubber |
| Anti-static device | 304SS | 304SS | 304SS |
Troubleshooting
Malfunction | Cause of malfunction | Troubleshooting method |
Operation jamming | 1. Drive device damage 2. Stuffing box installation tilt 3. Valve seat area blockage 4. Stem bending and seizing | 1. Maintain and repair the drive device 2. Loosen the stuffing box screws and reinstall the stuffing box 3. Turn the handwheel and switch several times in small increments 4. Rectify or replace the stem (please contact our company) |
Valve seat leakage | 1. The valve is not fully closed 2. Incorrect setting of the drive device limit switch 3. Sealing surface damaged due to abrasion | 1. Operate the valve to the fully closed position 2. Adjust the limit switch of the drive device appropriately 3. Please contact our company for repair |
Stem leakage | 1. Stem seal damage 2. Stem damage | 1. Replace the stem packing 2. Repair or replace the stem (please contact our company) |
Online Message
If you are interested in our products, please leave your email and we will contact you as soon as possible. Thank you!
Recommend Products
At present, it can produce more than a dozen series of more than 1,000 specifications of safety valves, power station valves, extraction check valves, gate valves, ball valves, check valves, butterfly valves, drain valves, balance valves, and regulating valves of different types and specifications.







